One of the many puzzles presented by the 2017 general election campaign and result is what looks to some like a return to something resembling the stable two-party system of earlier decades.
In 2017, the Conservatives and Labour took the votes of just over 82 per cent of the electorate, the highest combined share since 1970.
Did Theresa May and Jeremy Corbyn somehow contrive to end the drift towards electoral volatility and fragmentation of the party system that many observers saw in earlier elections and votes? Probably not.
That is the lesson I take from a presentation to the Social Market Foundation by Professor Jane Green of Manchester University. Thanks to the kind support of the ESRC, part of UK Research and Innovation, she was here to talk about findings from the British Election Study, which will be set out in a full in a forthcoming book (Fieldhouse et al: Electoral Shocks: Understanding the Volatile Voter in a Turbulent World). You can watch the whole talk here.
On the basis of Prof Green’s talk, the book will challenge many of the assumptions about the 2017 election about voters that are still common at Westminster, and should go on the must-read list for anyone involved with or interested in politics.
The central message I took from the talk is that when you look beneath the headline numbers suggesting stability in the electorate’s choices, you see that voter volatility is not just continuing but actually increasing.
Broadly speaking, voters are less and less attached to parties: the days of people sticking reliably with a single party over multiple elections really are over. Younger voters in particular start out their voting lives with less attachment to any particular parties than previous generations did, and do not seem to be developing the habits of loyalty as they age. Parental attachment to parties is not being passed on as once it was.
Unlike conventional opinion polls, which take snapshots of different subgroups of the electorate at different moments, the BES can track the same voters over time. That allows Prof Green and her colleagues to reveal facts like this one: of those people who voted in the 2005, 2010, 2015 and 2017 general elections, only around 40% voted for the same party every time.
In other words, the majority of voters over that period switched party at least once. Britian is becoming a nation of swing voters.
The full implications of that sort of volatility remain unclear, but more detailed findings from the BES certainly challenge one of the prevalent ideas of political analysis common at Westminster and in much of the media.
That idea is that the 2017 general election presented voters with a stark ideological choice between a traditionally Right-wing Conservative Party and a traditionally Left-wing Labour Party. That may indeed be how some of the participants in the election saw things. But it’s not how a lot of voters saw it.
The 2017 election saw more voters switching directly between the two big parties than ever before. In all, a little over 10% of those who backed either the Conservatives or Labour in 2015 then switched to vote for the other party in 2017.
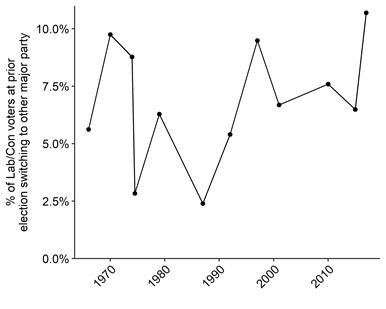
Far from politics polarising between two establishment parties locking in their traditional voters, the two big parties actually swapped voters at unprecedented levels.
That churn was reflected in a few constituency-level results, with Labour winning places such as Canterbury and Battersea from the Tories, and Conservatives gaining from Labour in Mansfield and Middlesbrough South and East Cleveland.
But seat-swapping rates did not match the vote-switching shown in the BES: beneath the surface of the first-past-the-post electoral system, voters are on the move in large numbers.
For those interested in the fine details, and wondering whether Theresa May or Jeremy Corbyn did best at attracting people from the other side, Prof Green’s Manchester colleague Jonathan Mellon says that around 12% of 2015 Conservative voters switched to Labour in 2017, while 9% of Labour’s 2015 voters switched to the Conservatives.
As Dr Mellon notes, the difference there is not huge – the real point is that there was substantial switching in both directions.
And my speculation is that this trend towards volatility and switching means the big parties will be ever less able to rely on their past supporters in future elections and will thus have to seek greater electoral rewards by increasing their appeal to other parties’ voters.
In other words, far from signalling an end to the age of volatility in politics, the 2017 general election may just have been the beginning.
